Background
Since 1994, laboratory testing in the United States has followed a 2-tiered serologic analysis algorithm, referred to as Standard Two-Tiered Testing (STTT) as summarized in the CDC flow chart below.

While relatively specific, the immunoblotting portion of the STTT algorithm contains drawbacks such as lack of sensitivity in detecting acute infection, interpretation subjectivity, and technically challenging procedures.
There are several published studies that support the replacement of the STTT’s second-tier immunoblotting with a more sensitive and comparably specific methodology such as ELISA. This modified method is referred to as a Modified Two-Tiered Testing (MTTT) algorithm. Many of the published studies that support the MTTT algorithm are authored by thought leaders in Lyme disease:
“For the past 2 decades, the concept of a 2-tiered strategy aimed at high sensitivity and specificity has been widely used, but the current approach is insensitive during the first weeks of Lyme disease, and Western blotting can be complex to perform and interpret.”1
“This subjective reading and interpretation [of second-step immunoblots] can lead to erroneous positive results if weak bands are scored as positive in samples with negative enzyme immunoassay.”2
“The limitations of STTT have been thoroughly discussed in the scientific literature [refs]. Most limitations are associated with the second-tier immunoblotting and include subjectivity when scoring the assay and false-positive results when using IgM immunoblots [refs].”3
“During early infection…both [2-EIA algorithm] strategies were more sensitive than standard 2-tiered testing…”4
The power of ZEUS Borrelia MTTT®
A pioneer in testing for Lyme disease and the first organization to receive U.S. FDA approval of a Lyme disease test in 1989, ZEUS Scientific is uniquely positioned to make the benefit-driven promise of a MTTT algorithm a reality in the clinical laboratory.
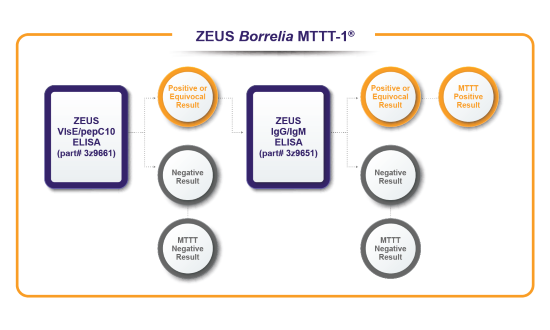
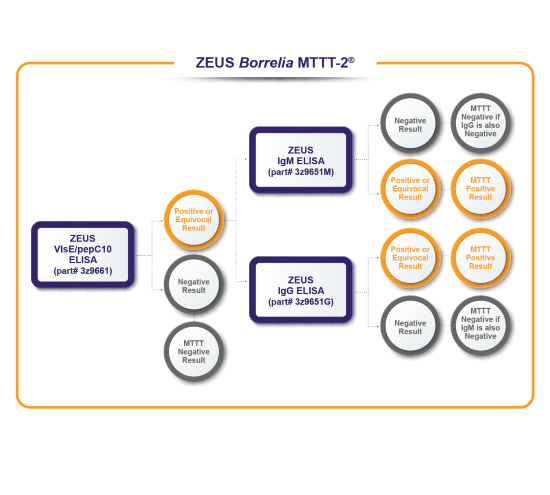
Validation of ZEUS Borrelia Modified Two-Tiered Testing (MTTT) algorithms
A well-characterized retrospective study cohort of serum samples comparing U.S. FDA-cleared ZEUS ELISA™ Borrelia burgdorferi Test Systems used in a STTT fashion vs. the same ZEUS ELISA™ Test Systems used in a MTTT fashion. 356 total specimens: 166 cases of Lyme disease, 90 specimens from diseases other than Lyme disease, and 100 healthy controls.

References
- Branda JA, Body BA, Boyle J, Branson BM, Dattwyler RJ, Fikrig E, Gerald NJ, Gomes-Solecki M, Kintrup M, Ledizet M, Levin AE, Lewinski M, Liotta LA, Marques A, Mead PS, Mongodin EF, Pillai S, Rao P, Robinson WH, Roth KM, Schriefer ME, Slezak T, Snyder J, Steere AC, Witkowski J, Wong SJ, Schutzer SE. Advances in Serodiagnostic Testing for Lyme Disease Are at Hand. Clin Infect Dis 2018 Mar 19;66 7:1133-1139.
- Aguero-Rosenfeld ME, Wormser GP 2015. Lyme disease: diagnostic issues and controversies. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 15:1–4. doi:10.1586/14737159.2015.989837.
- Mollins CR, Delorey MJ, Sexton C, Schriefer ME. Lyme Boreliosis Serology: Performance of Several Commonly Used Laboratory Diagnostic Tests and a Large Resource Panel of Well Characterized Patient Specimens. J Clin Microbiol 2016; 54:2726-2734.
- Branda, J.A., Linskey, K., Kim, Y.A., Steere, A.C., and Ferraro, M.J. Two-Tiered Antibody Testing for Lyme Disease With Use of 2 Enzyme Immunoassays, a Whole-Cell Sonicate Enzyme Immunoassay Followed by a VlsE C6 Peptide Immunoassay Clin Infect Dis. 2011 Sep;53(6):541-7.